Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition, where you get uneven tanning. To prevent it, it’s important to understand the causes.
Exposure to the sun’s rays can lead to dark spots and uneven pigmentation. Protect your skin with high-SPF sunscreen and stay in the shade.
Hormonal changes, like pregnancy or medication, can raise melanin production too. Reduce the risk with hormone-regulating skincare products.
Inflammation, from acne or eczema, can leave marks that take longer to fade. Follow a proper skincare routine and consult a dermatologist if needed.
Help reduce dark spots with ingredients like vitamin C, niacinamide, and retinol. These inhibit melanin production and help with natural exfoliation.
Good skincare practices are key. Cleanse your face twice daily, avoid harsh scrubbing, and use gentle exfoliants. Keep your skin hydrated with adequate moisturization. This will help maintain its natural protective barrier.
What Is Hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation is a skin condition where dark spots or patches appear. It’s caused by too much melanin, the pigment that gives color to our skin, eyes, and hair. These patches can be any size and shape and can be found anywhere on the body.
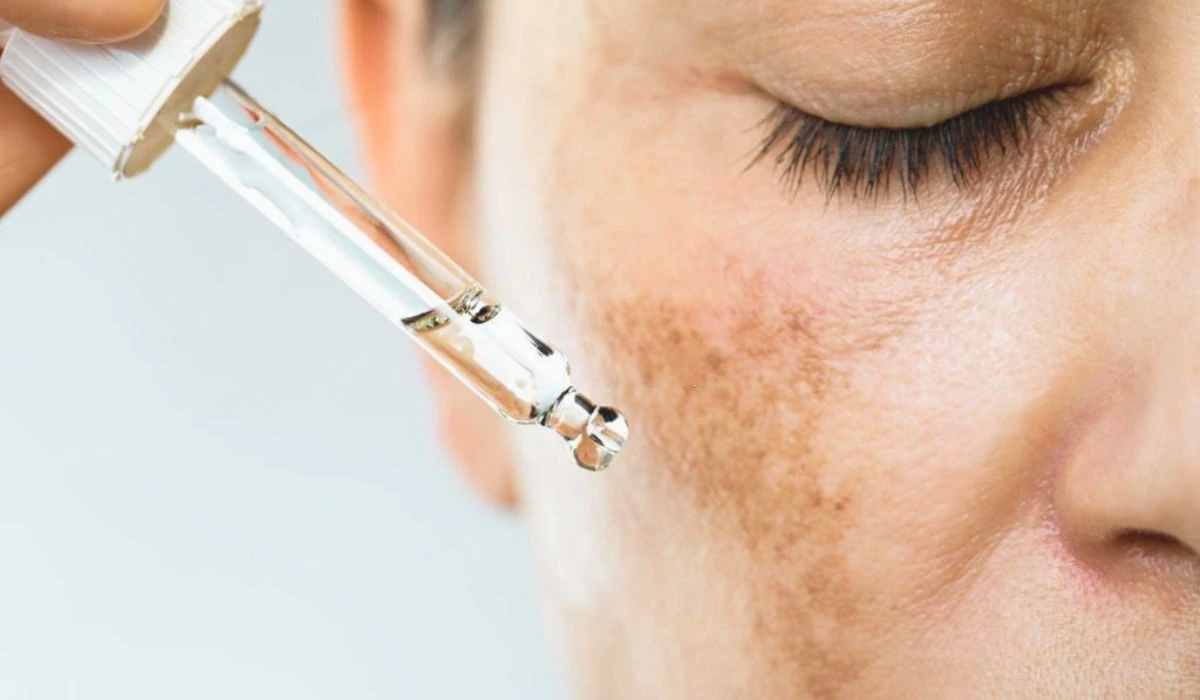
Sun exposure is the main culprit for hyperpigmentation. The sun’s UV rays cause an increase in melanin production to protect the skin from harm. This leads to dark spots in the areas that were exposed to the sun, such as the face, arms, and hands.
Hormonal changes can also contribute to hyperpigmentation. Pregnancy, certain medications, hormonal imbalances, and medical conditions like Addison’s disease can all cause an increase in melanin, resulting in dark spots.
Not all types of hyperpigmentation are permanent. Some, like acne scars or minor injuries, may fade over time with the right treatment. Other types, like melasma or age spots, may require more targeted treatments to see results.
Causes Of Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation, also known as dark spots or age spots, can be caused by various factors. Here are four common causes of hyperpigmentation:
- Excessive sun exposure: Prolonged exposure to the sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays can trigger the production of excess melanin, leading to hyperpigmentation. Sunburns and tanning beds can also contribute to this condition.
- Hormonal changes: Certain hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy or as a result of hormonal imbalances, can lead to hyperpigmentation. This type of hyperpigmentation is often referred to as melasma or the “mask of pregnancy.”
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation: Skin inflammation caused by acne, eczema, or injury can result in the overproduction of melanin, leading to dark spots in the affected area. This type of hyperpigmentation can occur in any skin type but is more common in people with darker skin tones.
- Genetics: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to developing hyperpigmentation. This means that their skin cells produce extra melanin, leading to an uneven distribution of pigment and the formation of dark spots.
? Sun exposure
The sun’s rays can damage your skin and cause hyperpigmentation. This is due to a rise in melanin production, resulting in dark patches. To avoid this, it is important to understand the causes and take precautionary steps.
Sunlight not only affects the surface of our skin but also penetrates deeper, activating melanocytes to produce more melanin. This can result in an uneven pigment distribution leading to hyperpigmentation. Plus, long or intense sun exposure can worsen existing patches, making them darker.
Some individuals are more prone to hyperpigmentation due to their skin type or genes. People with fairer skin tones have less natural protection against UV rays and are more likely to develop sunspots. Furthermore, those with a family history of hyperpigmentation may have an increased risk.
? Hormonal Changes
Hormones can cause melasma, a condition that looks like a mask on the face. It commonly appears on the forehead, cheeks, or upper lip. Certain medications, such as birth control pills, hormone replacement therapy, or conditions like PCOS or thyroid disorders, can disrupt normal hormone levels and lead to darkening skin.
? Skin Inflammation
When skin is inflamed, it releases chemicals triggering melanocytes to produce too much pigment. This causes hyperpigmentation. Plus, the inflammation affects the shedding of dead skin cells, causing them to pile up and worsen the issue.
Inflammatory conditions like acne, eczema, psoriasis, and dermatitis can cause post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Dark marks may remain after the inflammation subsides.
To avoid hyperpigmentation, address and treat the underlying inflammatory condition. A good skincare routine with gentle cleansing and moisturizing help keep the skin healthy and limit inflammation. Wear SPF to protect from hyperpigmentation.
How To Prevent Hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation, or the darkening of certain areas of the skin, can be prevented by following a few simple steps. These steps include:
- Protect Your Skin from UV Rays: Apply sunscreen with a high SPF every day, even on cloudy days. Wear protective clothing, such as hats and long sleeves, and seek shade during the peak hours of sunlight.
- Avoid Excessive Sun Exposure: Limit your time in direct sunlight, especially during the hours when the sun is strongest. If you need to be outside, try to stay in shaded areas and wear sunglasses to protect your eyes.
- Use Gentle Skincare Products: Avoid harsh cleansers and exfoliators that can irritate the skin and trigger hyperpigmentation. Opt for gentle, non-comedogenic products that are suitable for your skin type.
- Treat Your Skin with Care: Be cautious when shaving or waxing, as these methods can cause inflammation and lead to hyperpigmentation. Also, avoid picking or scratching at any skin imperfections, as this can worsen pigmentation issues.

